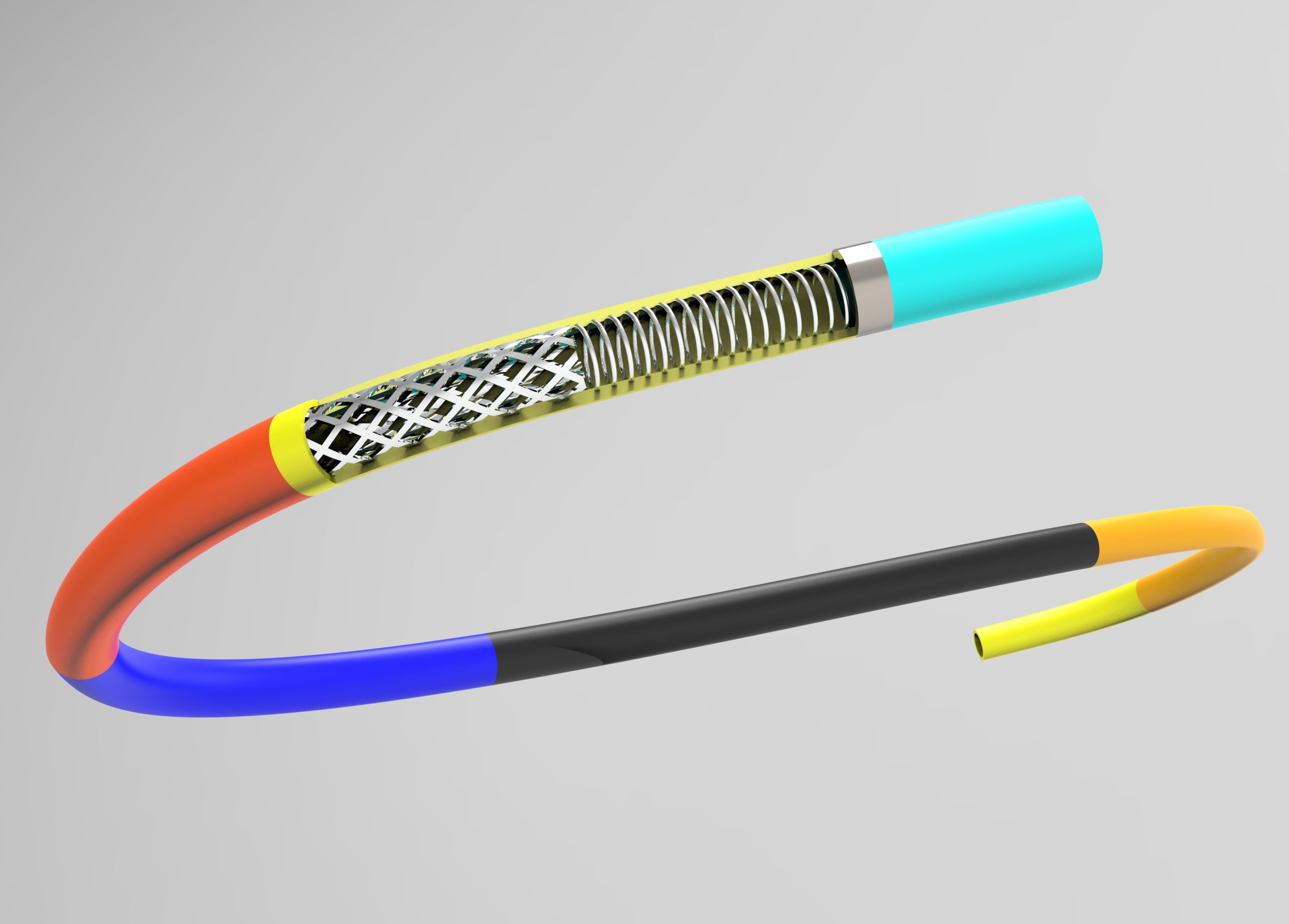
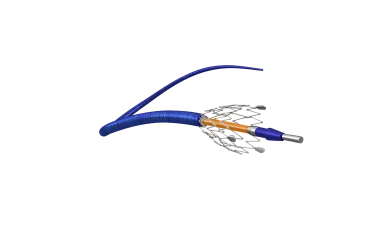
Stent delivery system Braided catheter
Establishing an access channel forinstruments to enter the body
Customizable in various sizes to meet different lesion requirements
Features
PTFE smooth inner wall- Reduces resistance, during device delivery
- Provides high-strength support,smoothly delivering stents, occluders,and other implantable devices
- Excellent kink resistance performance,flexibly adapting tovarious curved blood vessels
- Smooth pushing, reduce friction,improve passability
- Simultaneously,effectively reduces damage to the human body
- Clear positioning,ensuring precise stent release
Additional clinical applications of braided catheters:
- Cardiovascular & Structural heart:Aortic, mitral, tricuspid valve replacement delivery systems, Heart muscle cell therapy delivery system.
- Gastroenterology:Endoscopic suturing system, Laparoscopic mixing device for surgical sealant, Stomach wireless implant delivery system to prevent heart failure, lmplant delivery system for acid reflux disease.
- Neurology:Neurovascular guiding catheter, Clot Retriever device for acute ischemic stroke
- Gynecology:Fertilization delivery system, lntroducer of vaginal mesh implant, Ureteral stent delivery
- Pulmonary:Delivery system for artificial larynx, ENT navigation system.
Technical Parameters
- Catheter outer diameter: 5-28F
- Inner and outerdiameter tolerance: ±02-0.05mm
- Catheter length:500-2600mm
- Catheter tensilestrength: 30-300N
- Minimum catheter bending radius:10mm
- Catheter elongationrate: 0-5%, customizable (10N constant tension applied to both ends of the tubing)
- Catheter surface treatment: Hydrophilic coating
- Catheter reinforcement structure:Steel wire mesh, nylon wire mesh
- Catheter materials:PTFE, Pebax, PE, Nylon, PU, SUS
- Catheter radiopaque materials:Platinum-iridium alloy marker, tantalum marker, barium sulfate, tungsten, bismuth oxide
- Catheter layers: 3 layers, 4 layers, 5 layers
- Catheter hardness:TPU, PEBAX (25D – 72D)
Our Collaborative Approach
Related products
Braid & Coil Reinforcement Tube
The Demax Braid & Coil Reinforcement Tube is an innovative medical device designed to provide enhanced strength and flexibility for a wide range of medical applications. Crafted with precision and utilizing advanced materials, this reinforced tubing offers exceptional performance and reliability, making it an indispensable tool for medical professionals in various clinical settings.
ETFE Tube
ETFE tubes manufactured by Demax are crafted from high-quality ethylene tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE) polymer.
This fluoropolymer material offers exceptional chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for medical device applications.
ETFE tubes undergo precise extrusion processes to achieve consistent dimensions, smooth surfaces, and reliable performance in medical settings.
Microcatheter
Features:
1. PTFE inner layer allows for smooth passage for embolic agents;
2. Optimal trackability through tortuous anatomy;
3. Available in pre-shaped tip shape configurations for vessel engagement;
4. Four shapes provides more option for clinical usage;
5. 2.0F/2.2F/2.6F/2.8F models are available;
6. Hydrophilic coating technology, smoothly through the lesion.TPU Tube
Demax TPU tubes are meticulously crafted from Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), a premium synthetic polymer renowned for its exceptional elasticity, durability, and resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and environmental factors. This composition ensures the tubes’ longevity and reliability, even in the most demanding conditions. Demax’s commitment to quality extends to every aspect of their manufacturing process, from sourcing the finest materials to employing advanced production techniques. The result is a TPU tube that meets stringent industry standards, providing customers with confidence and peace of mind in their critical applications. Whether in medical procedures, laboratory experiments, or industrial processes, Demax TPU tubes deliver unmatched performance and durability, making them the preferred choice for professionals across various sectors.